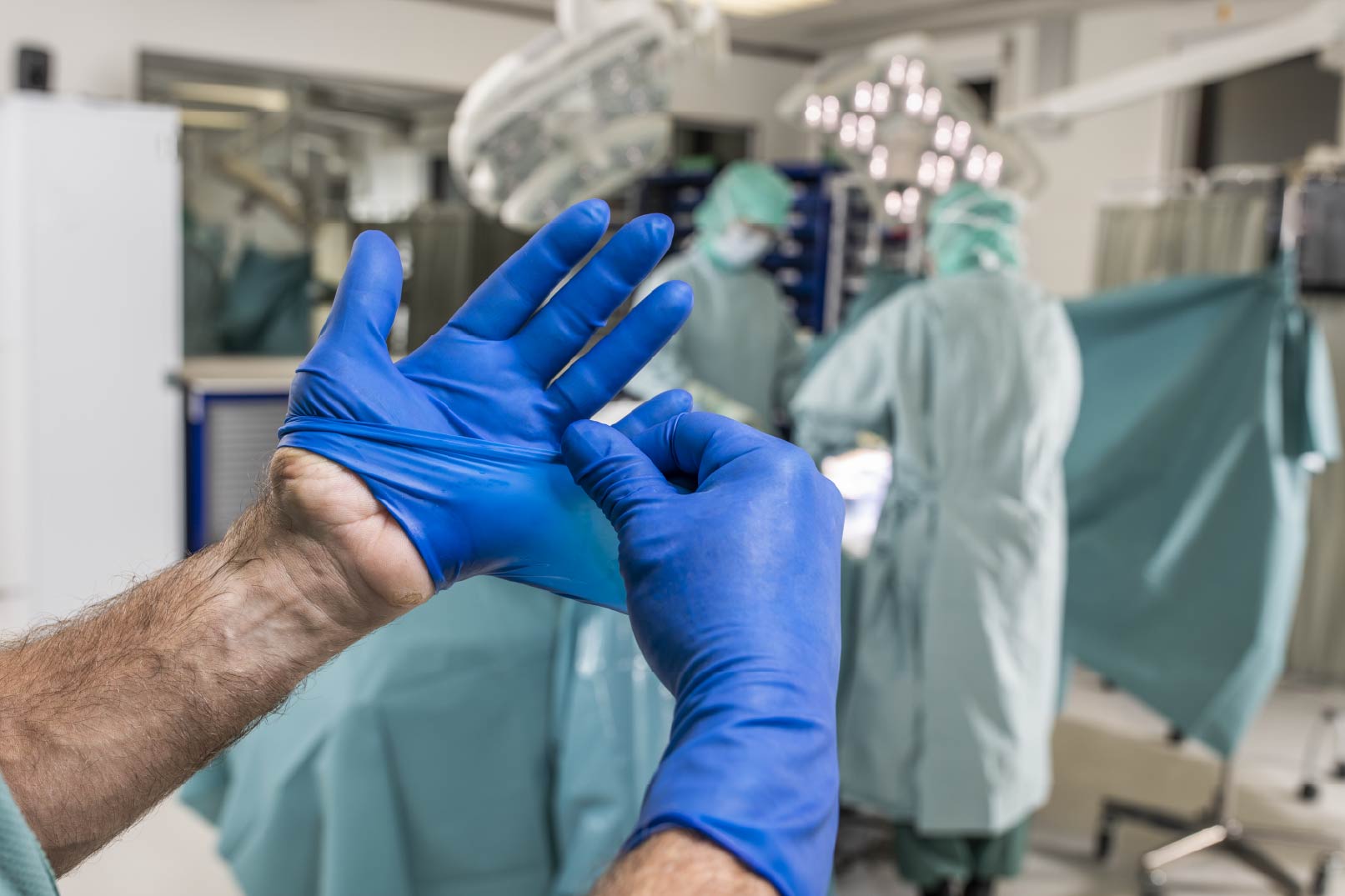
Improving surgical gloving practice is about embracing a culture of safety and leading the OR team to the most effective hand protection.1
Communication is critical
Preventive measures to reduce the risk of SSI, such as clean theatres, laminar air flow, good draping and skin prep, and so on, are protocol driven but rely very much on open communication policies in the OR and the surgeon setting that tone for the entire team.

이 에피소드의 내용
수술실에서 HCP를 보호하는 동시에 위험을 최소화하고 환자에 대한 감염을 예방하기 위해 안전하게 운영하는 방법에 대한 모범 사례 지침입니다. 게스트 네이선 쿰즈(Nathan Coombs)는 더블 글러빙 연습이 수술실의 표준 안전 조치에 어떻게 부합하는지 설명합니다.
Communication into practice
Ensuring safe OR practice also demands that gloves are donned properly, including double gloving and using a correct donning technique. The senior surgeon is responsible for staff, and should set the standard of practice for everyone in the OR.
Reality: Glove barrier breaches
Glove barrier breaches happen in the OR whether the injured party realises it or not. Sometimes only when removing surgical gloves does the wearer find that the gloves have been compromised. Double gloving helps protect the sterile inner glove – and hand – from bacterial contamination and keeps patient and OR staff safer, especially when an indicator glove system shows when the outer glove is breached.1
Reality: Tackling tactile sensitivity
The surgical glove can affect the tactile sensitivity required, and, for Mr Coombs double gloving with high-quality surgical gloves in breast cancer surgery meant his tactile sensitivity was not affected compared to when single gloving when gripping and working with breast tissue.
For surgeons, their hands are everything. Double gloving offers an efficient, cost-effective way to add that extra layer of protection during surgical interventions.2, 3